Since the beginning of the AI revolution, the phrase “SEO is dead” has been appearing more often than before. The idea is that since AI allows you to find answers faster and more effectively than the traditional “Google it” approach, then the businesses will lose the incentive to invest in their visibility in search results. This concern has led to the emergence of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), a discipline focused on optimizing websites and content for AI chatbots.
Some experts believe that the future of online businesses lies in GEO rather than SEO—but is that really the case?
- In this article, we share our insights and experiences with AI-powered search and its future in the industry.
- We will also provide a link to a custom Looker Studio report to help you track how much traffic your business is receiving from AI.
- Additionally, we’ll explain why we believe it’s best to wait before investing in services to improve your visibility on AI chatbots—at least for now.
What is GEO?
GEO stands for “Generative Engine Optimization”, a discipline focused on optimizing content and websites to enhance their visibility in AI chatbots and AI-powered search engines, such as ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity etc.
In other words, just as SEO improves a business’s visibility in search results, GEO does the same—but for answers provided by AI chatbots.
For those who have been in digital marketing long enough, the term ‘GEO’ might sound familiar, as it suggests a connection to geo-targeting. However, the similarity is only in the name, as geo-targeting refers to advertising directed at users based on their location and has no relation to AI.
SEO vs GEO
The basic advantage of GEO over SEO is simple: GEO provides direct answers, eliminating the need to look through search results.
While the differences and similarities between SEO and GEO are nuanced, they primarily revolve around seven key aspects:
| Aspect | SEO (Search Engine Optimization) | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) |
| Response generation | Optimizes for traditional search engines that provide a list of links in response to user queries. The answers are usually the most popular pages related to the query. | Optimizes content for AI systems that synthesize and prioritize information, helping AI generate quick and comprehensive responses. The answer is crafted to specifically answer the user’s query. |
| Content contextualization | Matches keywords to user queries and utilizes meta tags to make content easier to understand for crawlers. Without this, it is really challenging to rank high, even for high quality content. | Focuses on relevance and clarity to enable AI algorithms to generate accurate and comprehensive responses. The better the content is written the more likely it is to rank, regardless of meta tags, keywords etc. |
| Information synthesis | Aims to improve the ranking of individual pages. Usually the top 3 pages get the majority of the traffic. | Optimizes how AI integrates and synthesizes content from multiple sources to provide well-rounded answers. Any page can be cited, regardless of their ranking. |
| Algorithm adaptation | Requires continuous adaptation to search engine algorithm updates. It is now part of SEO specialists job to have been keeping up with Google’s algorithm updates. | Demands ongoing adaptation to the evolving capabilities, preferences, and methodologies of AI technologies. GEO specialists will have to keep track of a dynamic and constantly evolving industry. |
| Content formatting | Optimizes content by formatting it with headers, listings, splitting into smaller paragraphs. | Aims at clear structure and well-worded content ensure that AI can easily understand the meaning behind it. |
| Strategies | Relies on keyword research and technical analysis. | Requires analyzing AI-generated content structures, trending topics, citation patterns, and their evolution over time. |
| Performance tracking | There are multiple time-tested methods of tracking. SEO specialists monitor keyword performance, rankings, and other organic search metrics. | There is no single definitive method of tracking at the moment; however, some specialists monitor referral traffic from AI engines, cited sources, and response structures. |
A Notable mention: Search Generative Experience (SGE)
In response to growing interest in AI, Google has introduced Search Generative Experience (SGE), a hybrid approach that blends elements of SEO and GEO. SGE enhances visibility in search results but is limited to sections that summarize the results for users. In Google’s search results, this summary appears at the very top, making it a highly valuable position for businesses aiming to improve their visibility.
Will GEO replace conventional search?
If the AI removes the need for users to enter your website, does it mean your business is doomed? Not necessarily.
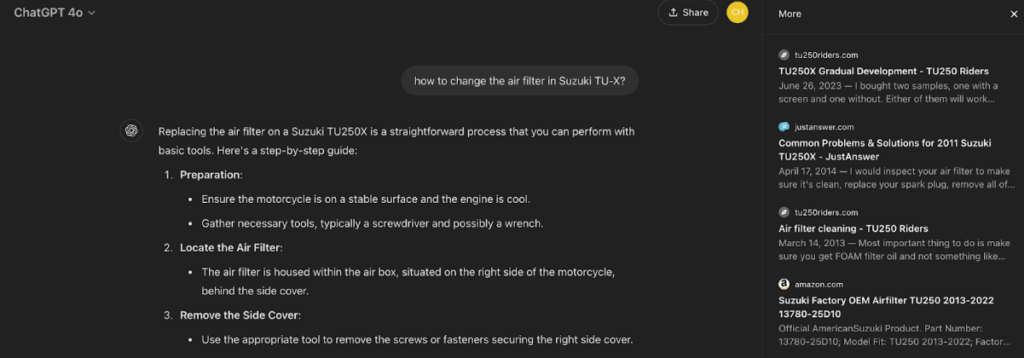
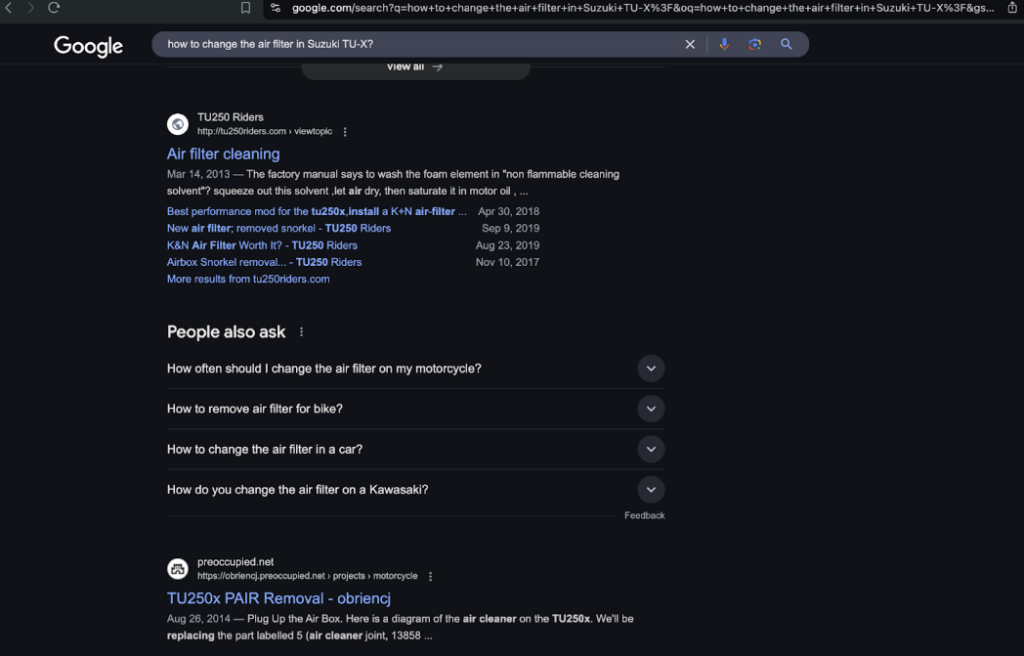
The answers AI generates are based on multiple sources, which are listed in the chat window. For example, if you run a motorcycle parts business and a potential customer asks an AI chatbot a question related to that topic, they might see your website cited as one of the sources. This increases the likelihood that users will perceive your brand as an expert in motorcycle parts.

 d-tags
d-tags